What are the Symptoms of a Brain Tumor
Summary
– Introduction
– Different kinds of brain tumors
– Symptoms of a brain tumor
– Brain tumor: combined treatments
– Poor prognosis of brain tumors
Brain cancers are rare cancers. These include peritoneal, eye, and testicular cancers, some sarcomas, trophoblastomas, vocal cord tumors, and other adrenal gland cancers.
Brain tumors are among the most common childhood cancers after leukemias (20%). In children, the primary tumors develop mainly in the posterior part of the brain. In adults, they are primarily located in the brain’s front.
Similarly, medulloblastomas that develop in the cerebellum or the nearby spinal cord are common before adolescence. They are even the most common brain cancers in children. Sarcomas and adenocarcinomas of the brain are exceptional.
As in heart cancer, where the heart cells are not affected, brain cancer does not affect the neurons themselves. In both cases, these specialized cells are no longer able to differentiate and multiply.
Various types of brain tumors
As with most cancers, brain tumors can be:
– either benign tumors that will spread slowly and remain isolated;
– or malignant tumors that will increase and are difficult to distinguish from the surrounding healthy brain tissue.
In addition to these two broad categories valid for any cancer, various subgroups of brain tumors differ in their characteristics.
Types of brain tumors
We distinguish :
– pituitary adenomas that develop in the pituitary gland (10% of primary tumors) and pinealomas that affect the pineal gland;
– chordomas that affect the cranial nerves or the cells of the spinal cord;
– Meningiomas (mainly benign) which develop very slowly in the meninges (protective envelopes of the brain) and which represent 40% of primary intracranial tumors;
– Osteomas that affect the bones of the skull;
– Schwannomas, which develop on Schwann cells, the sheaths that surround the nerves.
Glioma: the most common brain tumor
Overall, the most common benign brain tumor is glioma (50% of brain tumors). It is the one that affects the interstitial cells (glial cells) that support and nourish the gray matter (cortex).
These gliomas can be further subdivided into, among others
– glioblastomas (the most common malignant tumors) and in particular glioblastomas multi forms which are very virulent (they evolve in only 2 to 3 months) ;
– astrocytomas (rare but also rapid development) which affect the astrocytes and benign astrocytomas (20 to 30% of gliomas);
– ependymomas, which are more like cysts, or oligodendrogliomas, constitute about 20% of glial tumors.
Two-thirds of tumors are benign, including pituitary adenomas, meningiomas, and low-grade gliomas.
Symptoms of a brain tumor
Symptoms of brain cancer are highly variable as they depend entirely on:
– the location of the tumor (whether or not it affects a functional area of the brain);
– its size ;
– its aggressiveness (if it is metastasis, the tumor generally causes the sudden appearance of symptoms).
In the case of the cerebral tumor, the notion of benignity or malignity of the tumor remains relative. Indeed, a tumor, benign in itself, can cause severe symptoms (or even death) by compressing the neighboring structures.
Common symptoms of a brain tumor
Although one-third of brain metastases remain asymptomatic, a common symptom is a headache. They are characterized by their intensity, especially early in the day, and are felt on the tumor’s side.
They are usually accompanied by nausea and vomiting (especially in children) and disturbances of alertness. These signs of cancer are related to intracranial hypertension.
Symptoms specific to the location
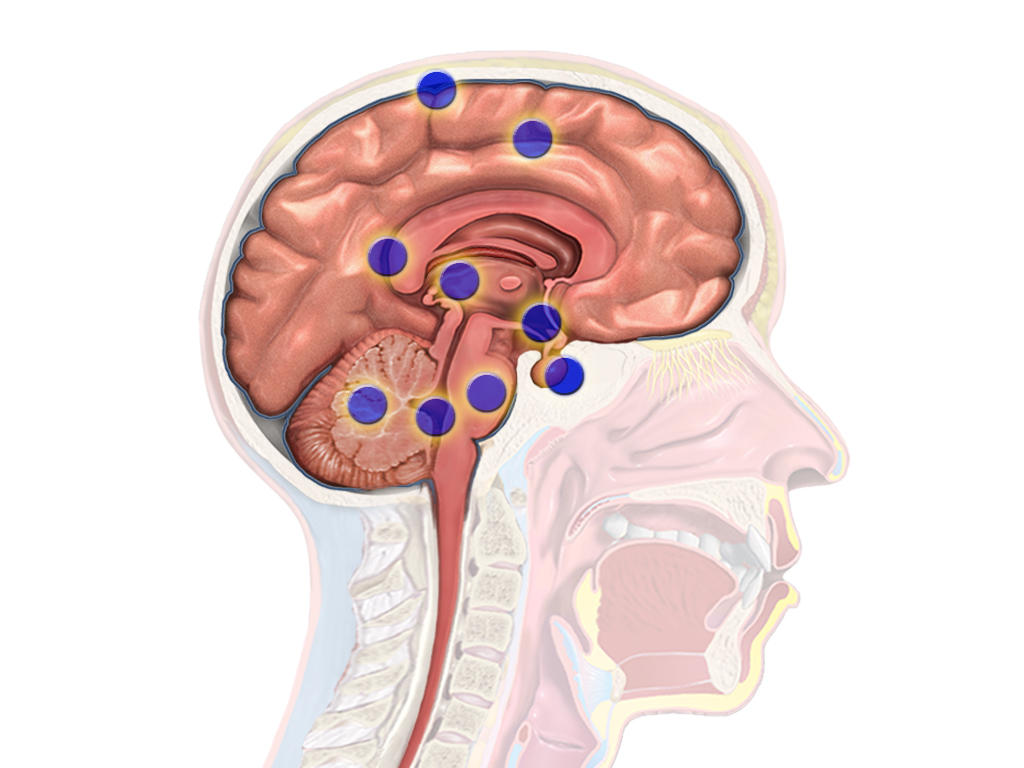
In addition to these headaches, brain tumors can cause other disorders such as:
– vision problems (including diplopia or double vision) and hallucinations if the occipital lobe (at the back of the brain) is affected;
– difficulty coordinating movement (especially if there is a tumor in the hemispheres of the cerebellum)
– hemiplegia (especially in the case of frontal tumors);
– sensory problems (in case of damage to the parietal hemispheres);
– speech difficulties (if the temporal areas are affected; the symptoms are then of late-onset);
– Nervous disorders, including epileptic seizures (if regions of the cortex above the brain tent are affected);
– dizziness (especially in the case of tumors in the central part of the cerebellum);
– amnesia of recent events (in case of frontal involvement), but clinical signs are usually of late-onset;
– mood disorders;
– an endocrine syndrome (in case of pituitary adenoma involvement) with possible:
◦ acromegaly (enlargement and magnification of hands and feet),
◦ hyperthyroidism,
◦ Cushing’s disease (excessive levels of hormones with glucocorticoid action),
◦ amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) or galactorrhea (milk flow).
However, extreme caution should be exercised as these symptoms may also have other origins than a tumor.
Specific symptoms in infants
In infants, there are a few symptoms that are typical of a brain tumor:
– an abnormally large skull before the age of 2 years (increased head circumference) ;
– a particularly marked tension in the anterior fontanel;
– a downward deviation of the eyes with retraction of the upper eyelid.
Brain tumor: combined treatments
Glioblastoma is usually diagnosed within three months. It takes two years after the first symptom to diagnose a benign astrocytoma. Treatment depends on this diagnosis.
The treatment of brain cancer is often based on the combination of several approaches
– surgery:
◦ to remove the tumor when possible without the risk of damaging nearby tissue,
◦ or at least to reduce its size to relieve some of the symptoms and optimize the effectiveness of other approaches;
– radiation therapy, which usually occurs after surgery;
– chemotherapy, which complements radiation treatment;
– Drugs to relieve symptoms as well as:
◦ corticosteroids to reduce tumor edema,
◦ anticonvulsants.
These therapeutic methods usually do not adequately cure malignant brain tumors. Still, they help contain the tumors for a few months.
If brain tumors are metastases, cancer will be treated primarily with radiation therapy.
Note: in the case of pituitary adenoma, either hormone replacement therapy will be used in the case of hormonal insufficiency or, on the contrary, hormone suppression therapy in the case of excess.
Recent research suggests that immunotherapy may be an effective solution with fewer toxic effects than other approaches. A patient’s T cells are treated and then reinjected to destroy tumor cells while sparing healthy tissue.
Poor prognosis for brain tumors
Brain tumors generally have a poor prognosis. Nevertheless, survival rates vary greatly depending on the type of tumor and its grade.
– People with glioblastoma have an average survival of 10 months.
– People with benign astrocytoma have an average survival of 5 years.
If you know a friend who is looking for information about brain tumor symptoms, please share this review with them. If this post has helped you in your quest for information, please also write us a few words in the section below.



whoah this blog is wonderful i really like reading your articles. Keep up the great paintings! You realize, a lot of people are hunting round for this info, you could help them greatly.